- 15 January 2025
- {{ views_count }} Views
- {{comments_count}} Comments
- {{rating_percentage}} % Ratings percentage
This site supports the ability to read text through highlighting
Alwaha for Child Development Services

The Role of Physiotherapy in Managing Pes Planus (Flatfoot)
Introduction
Pes planus, commonly referred to as flatfoot, is a condition characterized by the partial or complete collapse of the arch of the foot. This condition may be congenital (present at birth) or acquired due to factors such as injury, aging, or overuse. While flatfoot is often asymptomatic, it can lead to pain, discomfort, and biomechanical dysfunction in severe cases. Physiotherapy plays a critical role in managing pes planus, aiming to alleviate symptoms, improve function, and prevent complications.
Understanding Pes Planus
Flatfoot can be classified into two main categories:
Causes of Pes Planus
Symptoms and Complications
Symptoms:
Complications:
Physiotherapy’s Role in Managing Pes Planus
Physiotherapy aims to:
1. Assessment
The initial step in physiotherapy is a thorough assessment, including:
2. Exercise-Based Interventions
Strengthening Exercises
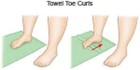
Stretching Exercises
Balance and Proprioception Training
Flatfoot can impair proprioception, leading to instability. Balance exercises such as single leg stands, wobble board exercises, and dynamic stability drills help enhance stability.
3. Manual Therapy
Physiotherapists may use hands-on techniques such as joint mobilization, soft tissue massage, and myofascial release to:
4. Orthotic Management
Although physiotherapists do not prescribe orthotics, they often work alongside podiatrists to ensure proper fitting and use. Custom orthotics or over-the-counter insoles can:
5. Gait Training
Physiotherapists can guide patients in correcting gait abnormalities caused by flatfoot. Proper foot placement, stride length, and weight distribution are emphasized to optimize efficiency and reduce compensatory patterns.
6. Education and Lifestyle Modifications
Special Considerations for Children
Pediatric flatfoot often resolves naturally as the arches develop. However, if pain or functional issues persist, physiotherapy interventions like those for adults are employed, with an emphasis on playful and engaging exercises.
Outcomes and Prognosis
With consistent physiotherapy, many individuals experience significant improvement in symptoms and function. While physiotherapy cannot restore the natural arch in most cases, it can effectively reduce pain, enhance mobility, and prevent further complications.
Physiotherapy is an integral part of managing pes planus, particularly for individuals experiencing pain or functional limitations. A combination of strengthening, stretching, manual therapy, and education empowers patients to manage their condition effectively. Early intervention and adherence to a tailored physiotherapy plan can lead to optimal outcomes, ensuring improved quality of life and mobility.
Trusted Resources for Further Reading
These resources provide comprehensive insights and evidence-based guidelines for managing pes planus effectively.
Comments({{ comments_count }})
{{ item.name }}
{{ item.created_at_format }}{{ item.message }}
Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply